War-time sexual violence exists for as long as wars themselves. Memory about mass sexual crimes during World War 2 still lives, for example, those committed by Wehrmacht and its allies on the occupied territories, by the Imperial Japanese Army (the phenomena of the so-called “comfort women”), by the Red Army in Hungary and Germany, etc. Despite the vast scale of those crimes, the post-war tribunals didn’t pay due attention to punishing the guilty, mostly due to political reasons and the overall underestimation of the role sexual violence plays in war. A pivotal shift in international laws regarding this issue happened only in the 1990s. It was the result of trials concerning the genocides in Rwanda and ex-Yugoslavia where hundreds of thousands of people suffered sexual violence, mostly women and girls. Since then, wartime sexual violence started to be seen in categories of “war crimes”, “crimes against humanity” and “crimes of genocide”. This is how the perception of the nature of wartime sexual crimes changed. They began to be characterized as a “method”, “tool”, “weapon”, or “tactic” of war or genocide.
Since the full-scale Russian invasion of Ukraine on the 24th of February, the topic of sexual violence flooded the media, political, military, human rights advocacy, and research discourses. Their foci are forms and consequences of sexual violence committed by Russian servicemen in Ukraine. This article focuses on its nature and functions, thus answering the question of whether Russia uses sexual violence as a weapon in its war against Ukraine.
Warning: this text contains depictions of sexual violence
Challenges of documenting
Since Russian aggression against Ukraine is ongoing, the picture of crimes, committed by Russian soldiers, is incomplete. In this picture, sexual violence is a part of large-scale and systematic crimes against the Ukrainian population which, according to the Ukrainian Prosecutor General’s Office data, there are more than 71 thousand as of today. But unlike the destruction of architectural objects, murders, and injuries which can be seen visually and documented, sexual violence is among the most hidden consequences of the war.
Despite that, information about sexual violence committed by Russian servicemen is now documented by both Ukrainian and international human rights organizations, particularly the UN, Human Rights Watch, Amnesty International, Center for Civil Liberties, JurFem, LaStrada, Women’s Perspectives, and others who provide support to the victims. Many publications in foreign media contain interviews with victims themselves. Another important sources of information are intercepted talks of Russian servicemen that are regularly published by the Ukrainian Security Service. In them, occupiers discuss various crimes committed on Ukrainian territory, including sexual ones.
Data on sexual violence and its perpetrators is also spread by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Prosecutor General’s Office. In particular, they report to Ukrainian society about the number of cases investigated, charges put forward, and first sentences. They also inform about coordination between different state institutions and cooperation with Western partners to oppose war-caused sexual violence and help the victims. However, not all officials showed a proper level of responsibility while communicating this sensitive subject.
In April 2022, the former ombudswoman Ludmyla Denisova came under criticism from media workers and NGOs. She was advised to “choose every word more carefully and thoroughly”, especially when talking about sexual violence against children, and report about the procedural actions concerning every case publicized. Soon, Denisova was fired from the ombudswoman’s position. That bolstered further speculations about the topic of sexual violence during the war. Both number of cases voiced by Denisova – she claimed hundreds of incidents back at the beginning of April – and their truthfulness were put in doubt. She found out about most of them from calls on the hotline for psychological help for those who suffered because of the war, created with the support of UNICEF. Denisova explained that she couldn’t pass all information known to her to law enforcement because she didn’t have consent for that from the victims.
“Denisova case” demonstrated the challenges Ukrainian society faces now with documenting, investigating, and communicating war crimes. The rights and interests of victims and their close ones should be at the center of these processes. There might be human tragedies behind every published case, that’s why each one deserves proper attention and checking, not silence and devaluation. Because the latter is precisely Russia’s strategy in its information war against Ukraine. Kremlin politicians and propagandists used the “Denisova case” to undermine not just her words but all information concerning sexual crimes of Russian servicemen in Ukraine, published by the Ukrainian side.
Specificity of sexual crimes in Russia’s war against Ukraine
After the occupation of Crimea by Russia and the beginning of the war in Donbas, the Ukrainian prosecutor’s office and police started documenting sexual crimes related to it[1]. In three years of intensive work (2014-2017), the Eastern Ukrainian center for civic initiatives collected information about 175 cases of sexual violence against men and women by illegal military formations. It included rape and threats of rape, sexual torture, forced nudity, threats of sexual nature, forced prostitution, threats and attempts of castration, etc. But after the full-scale Russian invasion of Ukraine on February 24, sexual violence committed by Russian servicemen acquired a different scale, intensity, and character.
First, sexual violence became widespread. It’s difficult to talk about the exact number of victims. As of today, the Ukrainian Prosecutor General’s Office investigates around 155 cases of sexual violence. And that number is merely the tip of the iceberg in the context of the overall scale of sexual violence because it includes only cases with clear consent on procedural actions by the victims.
Most victims aren’t willing to testify for various reasons. Some are afraid of stigmatization, victim-blaming, and mistrust of their words. Some people want to push painful memories out to avoid traumatizing themselves and their close ones. Some don’t believe in justice. Others are afraid to testify while the war is ongoing because they live in fear of occupiers returning and possible revenge for shedding light on their crimes. Some lack the resources to start a long and exhausting fight for justice. Thus, the number of those who suffered from sexual violence may be not hundreds but thousands, considering how many Ukrainians are now in Russian captivity or on temporarily occupied territories of Ukraine.
Second, sexual violence has become a tool of terror not against certain groups but against the whole population of the occupied Ukrainian territories. The victims are now not only women and men, like in previous years, but also children and the elderly. After breaking into the home of 75-years old Ludmyla near Kherson, the enemy soldier brutally beat and raped her. Another 83-year-old woman was raped by a Russian soldier in front of her husband, bedridden due to an illness. According to the UN data, the youngest currently known victim is only four years old. Instances of gang-raping girls aged 9 to 11 are known in Bucha, Kyiv region. It’s also known from the talks among the Russian military, intercepted by the Ukrainian Security Service, that 10 of their soldiers raped a 12-year-old girl in the Luhansk region, and three others – a 16-year-old girl. Among the victims, there are also boys, particularly an 11-year-old, raped in front of his mother.

A woman carries food given to her by volunteers on her late son's baby carriage in front of destroyed houses in a village near Kherson on January 31, 2023. Photo: REUTERS / Nacho Doce
Third, sexual crimes are committed with outstanding and demonstrative cruelty. This is evidenced not only by the age of the victims and the presence of the members of vulnerable groups among them – children or the elderly – but also by the dynamics and manifestations of that violence. In many cases, it is not a brief act but may go on for hours, days, or weeks, taking a shape of sexual torture to satisfy the aggressor. It is especially typical for sexual violence in places of forced detention. The UN Human Rights Monitoring Mission in Ukraine documented in its report the testimony of a man who was kept near Olenivka in the Donetsk region. He stressed that occupiers attached wires to his genitalia and nose and conducted the electricity: “They simply had fun and were not interested in my replies to their questions.” Victoria, 42-years-old from Kyiv region, was raped all night long, despite her begging to let her go. It’s also typical that rapes are accompanied by murdering men that try to defend their wives, and raped women themselves. Some victims had their teeth knocked out, hair cut off, limbs broken, face and neck cut, fingernails torn out. A separate kind of cruelty is raping children in front of their parents and vice versa, about which we'll speak in more detail later in this article.
All aforementioned and other indicators analyzed later in the article, are enough to affirm that sexual violence committed by Russian servicemen has features of a weapon in the war against Ukraine.
Carnival of violence
Sexual violence by Russian soldiers should be viewed not as a separate phenomenon but as part of a wide repertoire of violence against the civilian population on occupied Ukrainian territories which includes robberies, kidnappings, deportations, beatings, forced detention, attacks on energy infrastructure, destruction and damaging of medical facilities, libraries, museums, memorial sites, educational institutions, residential buildings, etc. Thus, sexual violence is one of the ways to demonstrate authority, terrorize, humiliate, intimidate, demoralize the “enemy” and reduce their will to resist. That’s why it takes grotesque and demonstrative forms.
Perpetrators act in ways that make victims realize the meaning of the violence for their torturers. It’s achieved, for example, by the perpetrators' vocabulary which underlines the political significance of violence. Victims are let know that they are targeted because of their political views, Ukrainian national identity, or their relatives’ affiliation with Ukrainian military or administrative institutions. For instance, on April 3 a mother of four in the Kherson region was raped for 12 hours by two Russian soldiers who were calling her a “Banderite”, possibly because her husband served in Ukrainian Armed Forces at the time.
According to Iryna Didenko, a prosecutor in the Prosecutor General’s Office, there are known instances when Russian occupiers purposefully targeted for rape wives of Ukrainian servicemen, possibly trying to undermine their morale and masculinity. Another demonstrative form of sexualized violence was shaving the heads of Ukrainian servicewomen. One of them, Anastasia, recalled: “They made us undress fully and squat in the presence of men. Shaved us bald.” Pictures of the women released from Russian captivity on April 2 shocked not only their relatives and colleagues. Visual marks of torture committed against them were kind of a message to the Ukrainian community in general about the values and intents of the enemy who doesn’t shun any methods to achieve the goal.
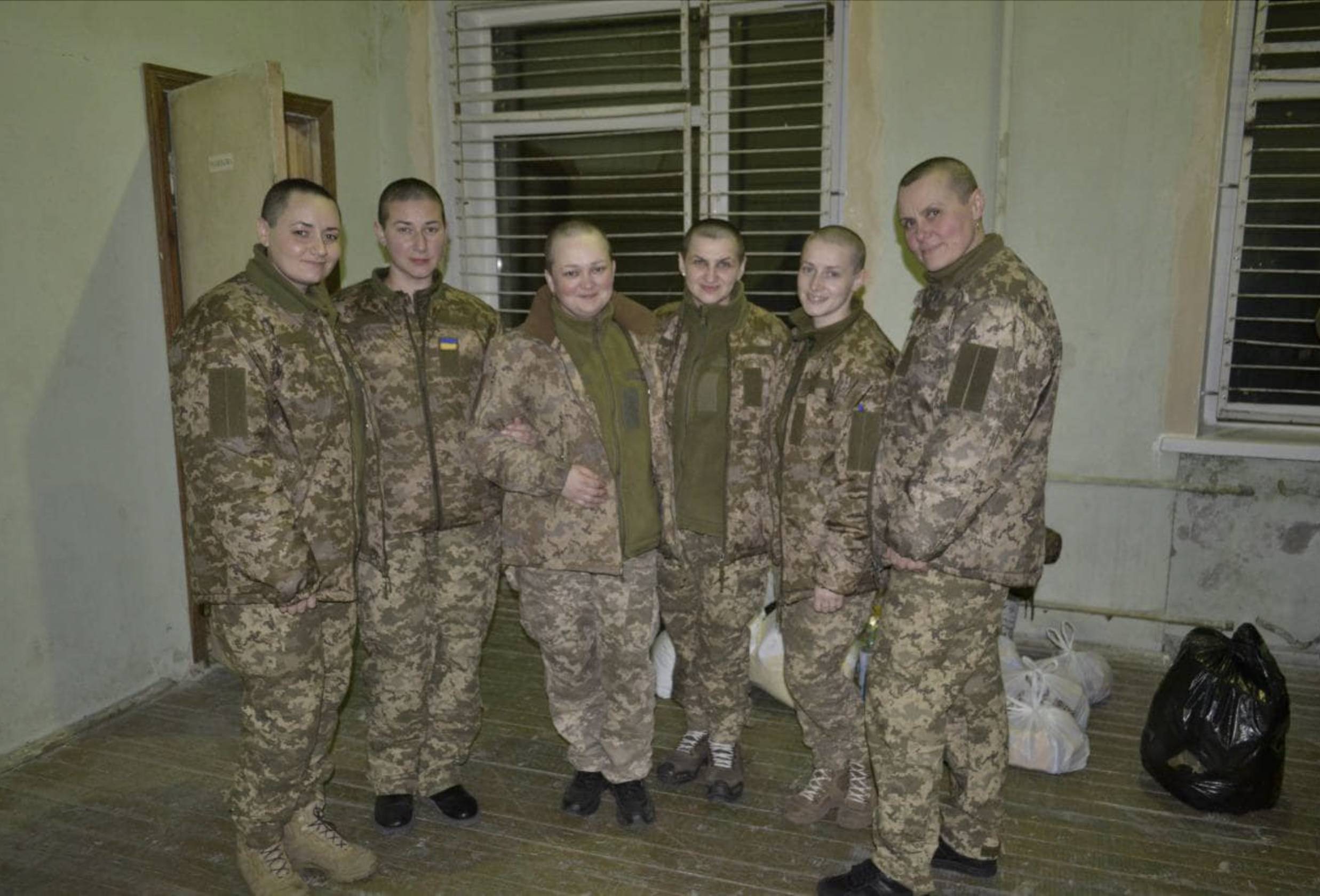

The Russians forced female military servicemen who were captured by the Russian Federation to undress, squat down, and then shave their heads. Photo: press service of the Ministry for Reintegration of the Temporarily Occupied Territories of Ukraine
Sexual violence of Russian servicemen against LGBT+ people in Ukraine also has a political tone. Possibly, it’s caused not only by the homophobia of particular soldiers but also by the aggressive anti-gender rhetoric and policies of Putin’s Russia over the last years. Kremlin propaganda pictures Ukraine as “a testing ground for unnatural phenomena” and “satanism”, against which Russia is “forced” to wage a “spiritual”, therefore a righteous war. As a result, Russian soldiers don’t conceal their enmity towards people with non-traditional sexual orientation in the occupied territories of Ukraine and use rape as a way to punish and humiliate them. This is evidenced by the “LGBTQ and the war” report, prepared by the “Our world” center in November 2022. According to the publication’s data, one of the victims recalls that two Russian soldiers broke into her home in the Kherson region during the night: “Are you those ‘pinks’?” though there was no pretext besides the fact that K. looks masculine. We were raped – me and my girlfriend – with the use of physical force.” Another part of the report mentions that after finding out about the homosexuality of a 31-year-old man in Mariupol, occupiers sent him to the penitentiary in Olenivka, Donetsk region. They disclosed information about his sexual orientation there, and because of that, he suffered multiple cases of sexual violence.
A characteristic feature of Russian occupiers’ sexual crimes is that they “need” the public to maximize the harm from their actions. This is what distinguishes war-time sexual violence from that committed in times of peace where it’s usually being done secretly to conceal the crime, and thus to avoid the responsibility. Criminals often don’t think about responsibility in the occupied territories. They are interested foremost in asserting their power and achieving both personal and military-political goals. This is why violence takes public forms and happens in the presence of relatives, friends, neighbors, or other people who are with the victim in a shelter or places of detention.
The presence of witnesses, especially close people, causes the victim additional suffering and at the same time traumatizes eyewitnesses because usually, they aren’t able to help. They are made to observe the torture silently and helplessly. As a result, witnesses become victims themselves and may live through trauma, similar in intensity and symptoms to the trauma of the so-called “primary” victims. For example, a boy aged 6 from Mariupol, whose mother was raped in front of him, went grey-haired, and a 15-year-old who watched violence against his mother had suicidal thoughts.
Sexual violence and military goals
Sexual violence becomes a tool of war when it meets the tactical or/and strategic interests of a fighting army rather than just the individual interests of particular soldiers. Meaning, when it’s not just a result of a lack of discipline in the army but a factor which, by the aggressor’s plan, brings the achievement of his military-political goals closer. In that case, commanders are aware that their subordinates commit sexual violence on occupied territories against the civilian population or prisoners of war but don’t oppose it effectively. They don’t implement preventive enlightenment or disciplinary action and don’t punish the perpetrators properly. Wayne Jordash, a British lawyer who consults Ukrainian prosecutors, stated that he saw the signs of commanders’ acquiescence in 30 cases he had reviewed. In some cases, commanders organized rape themselves. That happened with 42-year-old Victoria from the Kyiv region. She recalls that among three soldiers who knocked on her door during the night, there was a commander. He ordered the woman to go with them, explaining: “Our boys had some drinks and they want to relax.”
Some commanders try to use sexual violence as kind of a reward for their soldiers, a way to encourage them and boost their morale, especially with low-motivated soldiers like the mobilized ones. At the same time, sexual violence may be perceived by commanders as an acceptable and “safe” way to channel soldiers’ rage and frustration caused by defeats on the battlefield and unhappiness with the conditions of the service. Hence, it’s not a coincidence that Russian soldiers commit a lot of crimes against civilians when retreating from various territories, such as Lyman in the Donetsk region. Besides, gang rape acts as a tool to form cohesion and collective values in the army. As a thing that brings soldiers closer tying them by a shared experience of crimes. Considering that a lot of people who ended up in the Russian army, especially since the start of mobilization in September 2022, didn’t previously know much about the war and probably didn’t plan to participate in it, sexual violence, as well as other crimes, might be kind of rituals for military socialization.
Gang rape as a way to form army fraternity among Russian soldiers may be seen in the memories of the man who witnessed rapes in Irpin. He stressed: “ I didn’t hear anyone order this, but also, no one tried to stop them. On the contrary, they were encouraging each other; it was a joke to them. They were speaking Russian so we could understand them. I can’t remember the exact words, but I remember it meaning something like ‘our senior command allows us to do whatever we want unless you go to Bucha because no one is waiting for you in Bucha.’ I still don’t know exactly what that meant, but I can presume they belonged to a unit that was headquartered there but was coming to Irpin to act like this.” According to the witness, soldiers stripped, beat, and raped women. They killed four of them and ordered the eyewitness to put their bodies in the truck which they later set on fire.
Another way for commanders to encourage sexual crimes might be a conscious and purposeful demonstration of them to scare and demoralize the opponent. Very illustrative in this respect was the video of the castration and killing of a Ukrainian prisoner of war, published on Russian social media on July 28, 2022, committed probably by 29-year-old Ocur Suge-Mongush from Tuva. According to investigators from Bellingcat and Conflict Intelligence Team, the same criminal belongs to the Chechen group “Akhmat” and appears in various propaganda videos. After the video of castration, which has characteristics of a war crime, was published, there were no statements by the Russian military command assessing the actions of the executor and his partner who was filming. Neither the Russian military prosecutor’s office, nor any other competent institutions or politicians made a statement about an opened criminal proceeding regarding the video. According to the probable perpetrator himself, FSB released him after two days of investigation, saying that everybody depicted on video, executor of the crime included, were “Ukrainian soldiers.”
In other cases, Russian authorities not only protect their soldiers from criminal prosecution for war crimes in the occupied territories of Ukraine but also openly reward them, which simultaneously serves as an encouragement for new crimes, particularly for other military units. That happened with the 64th motorized brigade that was stationed in Bucha and became notorious due to multiple instances of sexual violence, even against children. By Putin’s decree of April 18, 2022, it received an honorary guards status for “mass heroism and honor, firmness, and bravery.”
“That’s a lie”: Russian authority discourse
From the moment when first accounts about rapes started circulating, Russian officials started denying everything. “We strongly refute it”, said Putin’s press secretary Dmitri Peskov on March 1, 2022, reacting to the statement by the International Criminal Law about the Russian army’s war crimes in Ukraine. In a few weeks, he claimed, “We don’t believe the information [of Ukrainian Prosecutor General’s Office] about raped women at all. That’s a lie.” Russian officials turned to categorically deny that Russian soldiers committed sexual crimes in Ukraine on the international stage as well. For example, at the UN meeting about the situation in Ukraine on April 4, Russian representative claimed that such information was spread to “distort facts and discredit the special military operation.”
Another UN meeting on June 6 started with the report by Pramila Patten, Special UN Representative on Sexual Violence in Conflict. She told about 124 cases of sexual violence related to the Russian full-scale invasion of Ukraine. In response, Russian representative Vasily Nebenzya claimed there was “no proof” to such accusations, and they are the “favorite tactic of the Kyiv regime and its Western colleagues.” When Pramila Patten published information that Russian soldiers use Viagra during rapes, Russian Ministry of foreign affairs released an official “refutation”, voiced by Maria Zakharova. According to her, such claims are “a perverted fantasy”, and they are “impossible to comment seriously.”
We can see similar rhetoric of absolute denial of sexual crimes committed by the Russian army in Ukraine in Russian media space. In June 2022, propagandist Olga Skabeeva, in her talk show “60 minutes” on the central Russian channel “Russia”, said: “It’s known for a fact that nobody raped anybody. In any case, not a single person accusing Russian soldiers of that has voiced neither name, nor surname, nor place of the event, nor time of the rape.” The host deceived her audience on purpose, probably knowing that by that time Ukrainian Prosecutor General’s Office already transferred to court the case about the rape of a woman, the suspect of which was Mikhail Romanov, a serviceman of the 239th regiment of 90th guards tank Vitebsk-Novgorod division of Russian armed forces.
Other Russian media people also stick to the official “lack of proof” version. Vladimir Solovyov, the Kremlin's top propagandist, wrote in his Telegram channel on May 4, 2022, that “informational henchmen of the Banderites are hyping an old “myth” about Russian army being rapists.” In his view, it was nothing else than a reanimation of a “lying” “myth” of the “Goebbels propaganda” that “appeared in Nazi Germany near the end of the war” about Russian soldiers allegedly raping all German women aged 8-80. Solovyov draws parallels between “fictional”, in his opinion, sexual crimes of Russian soldiers in 1945 with those of the Russian army in Ukraine now. In his desire to convince the audience of the falsehood of accusations against Russian soldiers then and now, the Kremlin propagandist resorts to denying one of the most documented and researched sexual crimes in the history of warfare, namely those committed by the Red Army in occupied Germany. According to Antony Beevor’s data, about 100 thousand women were subjected to sexual violence by the Red army soldiers in Berlin alone, 10 thousand of them died, mostly by suicide.
So, sexual violence by the Russian military in Ukraine after the start of the full-scale invasion on February 24, 2022, isn’t just a “byproduct”, i.e. the result of bad discipline, low morale, or abuse of power by individual soldiers and officers. Its systematicity, scale, organization, and forms prove the conscious and deliberate use of sexual violence to achieve the military-political goals of the Russian leadership. That’s why investigating and punishing the guilty should be a priority not just for Ukraine but also for international institutions, to help the victims, and achieve justice and durable peace.
Footnotes
- ^ Notedly, the perpetrators were on both sides of the conflict, for example, members of the dissolved Ministry of Internal Affairs "Tornado" company, some of whom were sentenced for rape. UN pointed to the instances of sexual violence used by Ukrainian law enforcement employees against the detainees of places of non-freedom in Donbas.
Author: Marta Havryshko
Translated by Yuriy Chernata
Cover: Kateryna Gritseva